Understanding Load Testing for Bamboo Trays
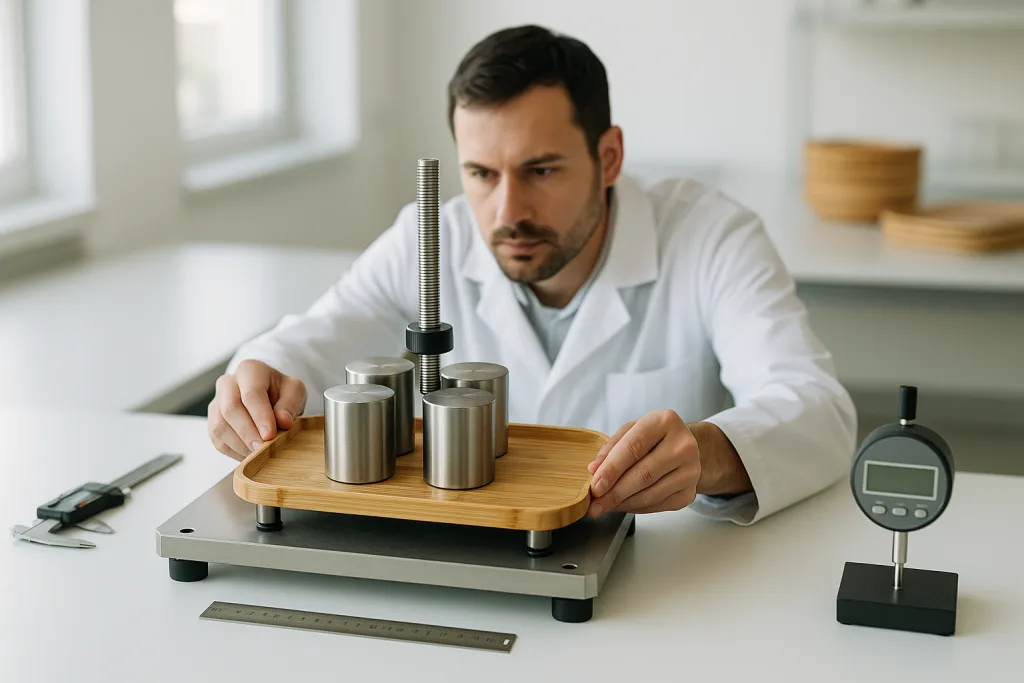
Load testing measures how much weight a bamboo tray can safely carry without breaking or deforming. This process is vital for manufacturers, hospitality brands, and retailers who need to ensure safety, durability, and customer satisfaction. A thorough bamboo tray load test evaluates not just the tray’s main surface but also its ribbed structure and handle strength, highlighting potential weak points.
Bamboo Wood Art, a leading manufacturer of bamboo and wood products, follows strict quality protocols, integrating sustainability with rigorous design validation. Whether for kitchen use, service in busy hotels, or premium retail displays, understanding load limits means fewer product failures and better end-user trust.
Lab Protocol for Bamboo Tray Load Test
Preparing the Bamboo Tray and Test Environment
Before testing, trays must be conditioned at 20–25°C and 50–65% humidity for at least 48 hours. This step standardizes moisture content (8–12%) and emulates real-world use. Position trays on a flat, rigid surface to avoid external support effects. All tests use trays with no visible defects and conforming to design specs.
Test Methods and Equipment
- Static Load Test: Gradually apply distributed weights (such as sandbags) to the tray’s surface until failure or excessive deflection occurs. Record each increment and observe deformation.
- Point Load Test: Concentrate weight at mid-span or weakest expected point—for instance, across rib gaps or at the handles—to simulate dropping or uneven weight distribution.
- Drop Test: Loaded tray is dropped from a set height (commonly 30–50 cm) onto a hard surface, simulating accidental knocks or falls in daily use.
- Handle Pull Test: Apply steadily increasing tension to each handle, measuring maximum force sustained before separation or cracking.
Measuring Deformation and Failure
Use a digital caliper and straightedge to gauge permanent warping, cracking, delamination, or fastener failure. Record maximum flex and visual changes at each load step. A tray is considered failed if it loses more than 3 mm flatness, visibly cracks, or no longer safely holds weight.
Rib and Handle Geometry: Impact on Load Capacity
Rib Designs and Cross-Section
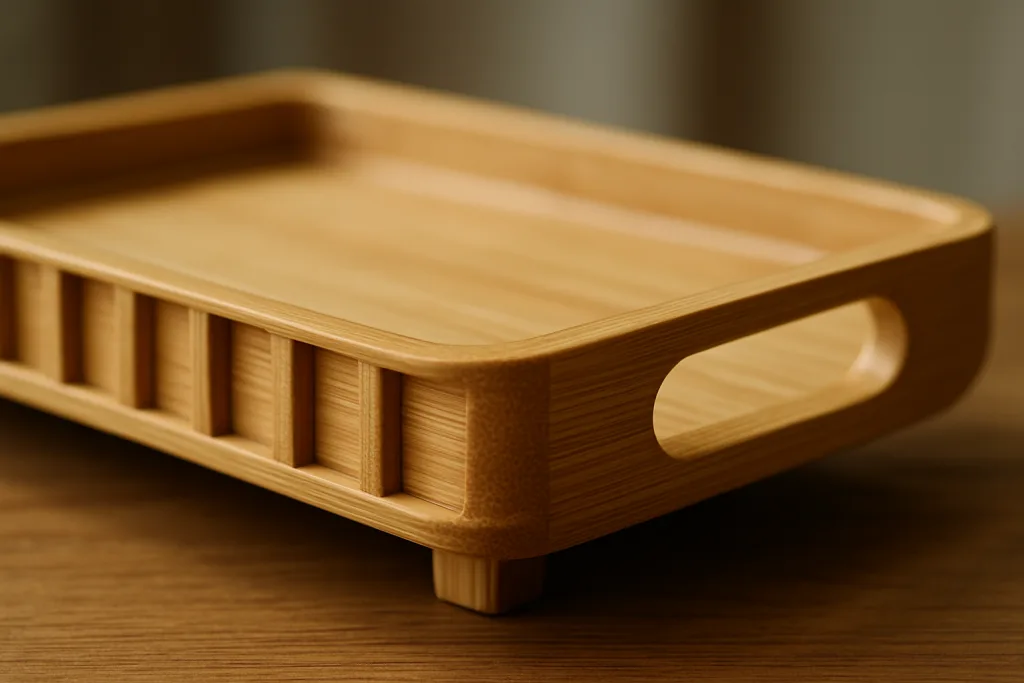
Ribs, or stiffening beams beneath the tray, provide essential structural support. The material, width, thickness, and number of ribs directly influence the bamboo tray weight limit.
Common rib designs include solid bamboo slats, cross-laminated panels, or finger-jointed sections. Moso bamboo is often selected for its high fiber density and stability. Standard rib dimensions for medium trays (350–450 mm length) are 18–30 mm wide and 8–12 mm thick, spaced 50–80 mm apart.
Handle Integration—Mortise & Tenon, Dowel, or Cut-in
- Cut-in Handles: Cut directly into the tray’s side walls. Quick to manufacture, best for light to medium loads.
- Mortise & Tenon Handles: Inserted into precision-cut slots. High resistance to pull load, ideal for heavier hospitality or restaurant use.
- Dowel Handles: Cylindrical bamboo rods integrated into tray sides, secured with hypoallergenic (food-contact compliant) glue for extra stability.
Geometry and Stress Distribution
| Feature | Geometry | Load Limit Effect | Best Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main Panel | Flat, multi-layer cross-grain | Up to 25 kg (large trays) | Heavy kitchen, service trays |
| Ribs | Parallel slats 20 mm wide/10 mm thick | Improves rigidity, +40% load | *All* size trays |
| Handles (Mortise/Tenon) | Reinforced joinery | Withstands dynamic pulls to 30 kg | Hospitality/multipurpose |
| Handles (Cut-in) | Integral to sidewall | 15–18 kg safe max | Light/prep trays |
Thicker ribs and reinforced joints ensure load is evenly distributed. Bamboo Wood Art’s CNC precision cutting maintains joint tolerances of ±0.3 mm, which minimizes stress risers and premature wear.
Failure Modes in Bamboo Tray Load Testing
Surface Cracks and Delamination
Bamboo trays may fail through cracking in high-stress areas or by layers peeling apart (delamination). Inadequate adhesive curing, low-quality resin (below E1-standard), or excess moisture can trigger early failure. Finished trays with food-safe water-based varnish offer added protection against moisture migration.
Rib Sheer and Buckling
Poor rib sizing or material inconsistencies cause ribs to fail under modest loads. Parameters to check include kiln-drying details (well-cured to 8–10% moisture) and slat uniformity. Look for ribs separating from tray panels or significant deflection during mid-span loading as warning signs.
Handle Separation
Most handle failures originate from weak joints or subpar adhesives. Proper mortise-and-tenon machining and the use of food-safe adhesives, such as D3/D4-grade PVA, reduce these risks. Handle tests should simulate real-world pulling and jolts, not just slow, steady force. Ambitious hospitality programs sometimes require custom handle reinforcements—Bamboo Wood Art can advise on these design upgrades.
Bamboo Tray Weight Limit: How Much Is Safe?
Establishing Safety Thresholds
Bamboo tray weight limits vary by size, design, and finish. Standard small trays (250–320 mm) safely carry 6–10 kg distributed load. Medium trays (350–450 mm) range from 12–18 kg. Large service trays (480 mm+) with extra ribbing and reinforced handles can support up to 25 kg safely. Always recommend a safety margin of at least 15% under lab-verifiable max values.
Impact of Finishing and Edge Profiles
Smooth, radiused edges and hard-wearing finishes (UV varnish, food-safe plant oils) prevent early splintering and absorb minor impacts. Bamboo Wood Art’s finishing process sands surfaces in three stages (180 → 240 → 320 grit) and applies a low-VOC water-based resin, maximizing both aesthetic and structural longevity.
Comprehensive Bamboo Tray Load Test Procedure
- Condition trays for minimum 48 hours at standard temperature and humidity.
- Visually inspect each tray for warping, cracks, or adhesive flaws. Reject defective samples.
- Apply static and point loads using calibrated weights, increasing in 1–2 kg steps. Record all readings.
- Document vertical deflection after each increment using a straightedge and digital caliper.
- Test handle strength via gradual pull and sudden jerk, measuring failure or heavy deflection.
- Drop loaded tray from defined heights, then re-inspect for damage.
- Designate pass/fail based on criteria: crack-free, <3 mm permanent warp, secure handles.
- Complete and file a detailed lab sheet for each tray type and batch.
Tip: It’s important to test both finished and unfinished trays to isolate the effects of varnish and edge treatments.
Spec Sheet Template for Bamboo Tray Load Testing
Recommended Spec Fields
- Tray Model/Size
- Material (e.g., 5-ply cross-laminated Moso bamboo)
- Finish Type (UV varnish, tung oil, etc.)
- Rib and Handle Geometry (dimensions, spacing, joinery)
- Moisture Content (%)
- Test Type (static, point, drop, handle pull)
- Max Registered Load/Deformation (kg/mm)
- Failure Mode (crack, delamination, joint separation, etc.)
- Safe Working Load (kg, with margin)
- Date/Operator/Batch ID
Consistent spec sheets prove compliance for B2B partners and smooth quality assurance for bulk orders. Bamboo Wood Art’s clients use tailored formats for hospitality, gifting, and specialty retail channels.
Best Practices for Safe and Durable Bamboo Tray Design
Choosing Sustainable, High-Strength Materials
Opt for 100% FSC- or PEFC-certified Moso bamboo. This variety offers a reliable balance of low weight and exceptional fiber strength.
Process Controls and QC Highlights
- Segregate by slat grain and color uniformity pre-lamination.
- Monitor kiln and press settings closely—overheating weakens fiber bonds.
- Check each glue line for continuity and adhesive bleedout, ensuring E0/E1 resin use to meet export standards.
- Apply edge profiles and finish coats evenly. Sand to fine grit levels for edge safety and finish adhesion.
Rely on sample tray testing for each large production run, especially when introducing new handle or edge geometries.
Load Testing for Bamboo Trays
Load testing for bamboo trays is a critical protocol in manufacturing and R&D. Following a practical, step-by-step lab method ensures every product shipped—whether for home kitchens or high-traffic restaurants—meets its rated bamboo tray weight limit safely. Rib and handle design, joinery selection, and finish type all contribute directly to maximum safe weight. By logging tests and referencing spec sheet templates, buyers and manufacturers set clear expectations and protect end users from unexpected breakage. Bamboo Wood Art exemplifies this practice, blending craftsmanship, eco-materials, and robust testing for the most demanding B2B scenarios.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the typical bamboo tray weight limit?
Small bamboo trays usually support 6–10 kg, while medium trays can carry 12–18 kg, and large trays with robust ribbing and handles may reach 25 kg safely.
How is load testing for bamboo trays performed?
It involves applying increasing weights on a conditioned tray, observing deformation, and testing handles. Static and point loading, as well as drop tests, are standard.
What are common failure modes during bamboo tray load tests?
Typical failures include surface or rib cracks, delamination, and handle separation due to weak joints or substandard adhesives.
Why does rib and handle geometry affect load limits?
Deeper or wider ribs and strong joinery distribute forces better, so trays resist bending and handles stay secure under heavy or sudden motion.
Which finish is best for bamboo tray durability?
Water-based UV varnish or plant oils (like tung or linseed) provide moisture resistance, reduce splintering, and prolong tray life in kitchens or restaurants.
What info should a bamboo tray load test spec sheet include?
Details like tray size, material, finish, rib geometry, test procedure, max weight, failure mode, and safe working load, plus date and batch number, ensure traceable results.