Introduction
It’s estimated that over a billion plastic toothbrushes end up in landfills every year—a staggering figure that spotlights a growing problem in daily oral care. Traditional plastic toothbrushes, typically made from petroleum-based plastics, can take hundreds of years to break down, leaching microplastics and additives into soil and water as they degrade. As environmental awareness spreads, eco-friendly alternatives like bamboo toothbrushes and bioplastic toothbrushes have surged in popularity, promising to curb our reliance on fossil fuels and reduce long-term waste. But which truly offers a greener solution for sustainability-minded households?
What Is a Bamboo Toothbrush?
Bamboo toothbrushes feature handles crafted from natural bamboo—a plant renowned for its rapid growth and renewability. Unlike hardwood trees, bamboo species such as Phyllostachys edulis (Moso bamboo) mature in just three to five years and require minimal pesticides or irrigation. Manufacturing typically involves harvesting mature culms, followed by drying, shaping, and sanding to produce a smooth, ergonomic handle. Some brands, including Bamboo Wood Art, use precision sanding and food-safe adhesives to ensure durability and reduce splintering. The result is a biodegradable product: the bamboo handle can decompose in a home compost or landfill environment within months, returning nutrients to the earth.
Looking to launch your own bamboo toothbrush line? Explore custom manufacturing options with our experienced bamboo toothbrushes manufacturer.
What Is a Bioplastic Toothbrush?
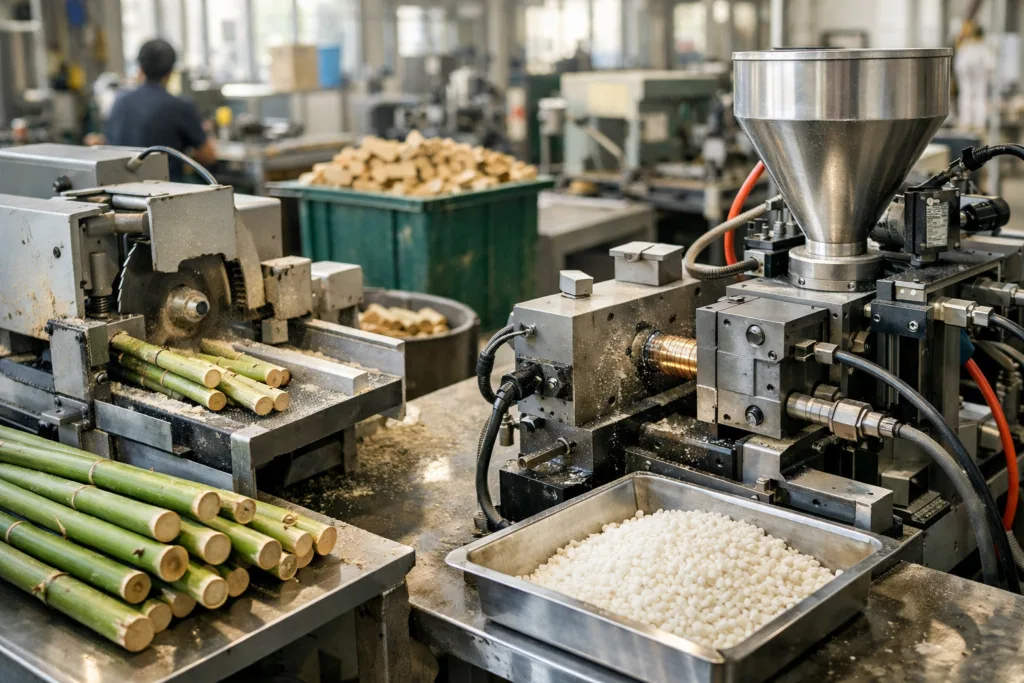
Bioplastic toothbrushes are engineered using plant-derived polymers instead of conventional petroleum-based plastics. Common feedstocks include corn starch, sugarcane bagasse, potato starch, or cellulose. These materials are processed into bioplastics such as PLA (polylactic acid), which resemble conventional plastics in look and feel but may offer compostable or recyclable end-of-life options. Depending on blend and additives, some bioplastics are industrially compostable, breaking down under high-temperature, controlled conditions. Others, especially those combined with traditional polymers or plasticizers, may be recyclable in specialized facilities. The manufacturing process still involves extrusion, molding, and finishing—mirroring many steps seen in regular plastic production, but using alternative feedstocks.
Environmental Comparison
| Factor | Bamboo Toothbrush | Bioplastic Toothbrush |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Sourcing | Bamboo is a fast-growing, renewable grass; harvest often supports local economies and requires less fertilizer and water. | Bioplastics source from crops (corn, sugarcane); may need significant farmland, fertilizer, and water—sometimes competing with food systems. |
| Manufacturing & Energy Use | Minimal processing, low energy input for crafting handles, bristles often remain conventional. | Processing crops to bioplastics can be energy-intensive, depending on technology and transportation. |
| End-of-Life Disposal | Bamboo handles are home compostable and biodegradable; bristles usually need removal. | Bioplastic handles may be compostable only in industrial facilities (not home compost); end-of-life can be tricky if mixed polymers or additives are included. |
The sustainable edge generally leans toward bamboo for renewable sourcing and low-impact processing, though bioplastics offer promise if properly composted or recycled.
Performance and User Experience
Both bamboo and bioplastic toothbrushes deliver sufficient durability for daily brushing routines, usually lasting three to four months as recommended by dentists. Bamboo handles feel natural and slightly textured, which many users prefer for grip and comfort. Bioplastic handles mimic the look and ergonomics of standard plastic, offering bright colors and designs. In terms of brushing effectiveness, both rely on similar nylon bristles, though bamboo alternatives can sometimes incorporate charcoal-infused bristles. For tips on maintenance, check out this guide on how to keep your bamboo toothbrush from molding.
Challenges and Limitations
Potential Environmental Downsides
Bamboo cultivation, while generally eco-friendly, may contribute to biodiversity loss if monocultures replace native forests, or if chemical treatments are overused. Bioplastics may require significant land and water inputs, and if sourced from food crops, can compete with global food supply. Some bioplastics include additives that hinder compostability, or may only break down in specific industrial settings—not backyard compost heaps.
Market Availability and Misconceptions
Consumers sometimes assume that all bamboo or bioplastic toothbrushes are fully biodegradable or compostable—which is often not the case. Nylon bristles remain a sticking point for both types, as they are usually petroleum-based and need to be removed before composting handles. For accurate environmental disposal, you might find this article on how to dispose of a bamboo toothbrush correctly helpful.
Manufacturing Standards
If you are sourcing bamboo products, make sure your supplier’s credentials are well-verified to ensure genuine sustainability. Learn more in How to Verify a Bamboo Manufacturer’s Credentials.
Which Is Greener?
Weighing the evidence, bamboo toothbrushes often edge out bioplastic counterparts for their lower manufacturing footprint, rapid renewability, and easier home compostability. Bioplastic options depend heavily on sourcing methods, additive content, and local composting or recycling facilities. That said, both offer tangible improvement over single-use plastics. For truly sustainable oral care, consumers should look for responsibly sourced bamboo, avoid chemical-laden products, and dispose of components properly.
Bamboo vs. Bioplastic Toothbrushes: Which is Greener?
Choosing between bamboo and bioplastic toothbrushes comes down to the entire life cycle: from how raw materials are grown and processed, to how they’re disposed of. Bamboo’s renewability and biodegradability make it an attractive choice, provided ethical sourcing is ensured. Bioplastics offer innovation and reduce fossil fuel reliance, but can fall short on compostability and overall footprint depending on production methods. Whichever you select, support brands that prioritize clear labeling and responsible stewardship at every step.
Conclusion
In the transition toward greener oral care, bamboo and bioplastic toothbrushes play vital roles in reducing landfill waste and plastic pollution. Smart choices mean considering not just the brush’s materials, but its full journey from farm field to bathroom, and ultimately, back to earth. Seek out detailed product information, dispose thoughtfully, and encourage manufacturers toward greater transparency. Every small step—like switching your toothbrush—adds up to a healthier planet.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does a bamboo toothbrush take to decompose?
A bamboo toothbrush handle can biodegrade in 4–6 months in home compost or landfill with proper conditions; bristles must be removed first.
Are bioplastic toothbrushes truly compostable?
Most bioplastic toothbrush handles require industrial composting facilities for effective breakdown; home composting may not work for all types.
Can bamboo toothbrushes grow mold?
Yes, if left wet or stored in humid areas, bamboo can mold. Store in a dry place and rinse thoroughly after use.
Do bioplastic toothbrushes contain any petroleum?
Some bioplastic handles are blended with conventional plastics or additives, so check labels for pure plant-based content.
Which toothbrush type is safest for sensitive gums?
Both types offer soft-bristle options. Choose a brush that fits your gum sensitivity and oral health recommendations.
How should I dispose of toothbrush bristles?
Regardless of handle material, nylon or mixed bristles should be separated and placed in regular trash unless local recycling permits.